Hiring SAP Developers 101: Everything You Need to Know
SAP should sit at the core of your enterprise resource planning because it drives finance, HR, logistics, and supply chains. However, the issue is that migrations to S/4HANA and cloud-based SAP solutions are pushing demand for skilled developers higher than ever.
In fact, analysts project resource needs to climb 75% in the coming years. This can leave you exposed if you hire poorly. So, to avoid this, we'll show you how to approach SAP development strategically.
But first, let’s define who these developers are.
Who are SAP Developers?
SAP developers are specialists who design, customize, and maintain applications across different SAP modules. Their work spans backend ABAP coding, SAP Fiori/UI5 frontends, and integration roles that connect SAP with external systems.
According to Zion Market Research, the global SAP services market is expected to hit $154 billion by 2030. This reflects just how important their expertise has become. For a quick overview of SAP, watch this short video on its ERP, cloud tools, and high-demand areas:
To see why this role matters so much for you, let’s look at why companies need them.
Why do companies need SAP Developers?
SAP developers are important because your enterprise resource planning systems rely on constant stability and adaptation. The reasons you need them are:
Core operations depend on SAP: Finance, HR, procurement, and logistics run on it. Any disruption or lack of developer support can stop daily core operations.
Customization: Standard SAP functions rarely cover your needs. Developers extend systems through ABAP coding and SAP Fiori to match unique workflows.
Integration: SAP must connect with CRMs, WMS, or payment platforms, and weak links can create delays and cost overruns. In fact, a Forrester study found that companies using SAP Integration Suite achieved 345% ROI in three years. This shows how the right integration approach directly impacts financial performance.
Efficiency: Automation built by developers cuts manual work and speeds up processing.
Compliance: Developers adapt systems to meet audits, tax laws, and reporting requirements across markets.
Migration: When you move from ECC to SAP S/4HANA, you must remediate custom Z-code, replace deprecated objects, migrate data, and rework integrations (CDS/OData, IDocs via PI/PO or CPI). Programs that skip code analysis and cutover rehearsals run over budget and schedule. Industry studies show about 65% of S/4HANA projects overshoot budgets and take roughly 30% longer than planned.
Now, let’s break down the actual responsibilities these developers carry.
Responsibilities and Work Scope of SAP Developers
The truth is, SAP developers keep your systems stable, scalable, and audit-ready. So, their responsibilities extend far beyond writing code.
The key areas you need to consider are:
Customization: Building Z-programs, enhancements, and user exits through SAP ABAP development.
Application development: Delivering reports, workflows, interfaces, and forms that align with functional requirements.
System integration: Linking SAP with non-SAP platforms through middleware like PI/PO or CPI. Plus managing SAP process integration, OData services, APIs, and EDI connections.
Testing and debugging: Performance tuning, error resolution, and QA support to avoid downtime.
Maintenance: Applying OSS notes, running patch cycles, and planning version upgrades.
Collaboration: Working closely with consultants, end users, and project management teams throughout development cycles.
Documentation: Producing technical specs and design docs so future teams avoid knowledge gaps.
For a first-hand look at daily work in SAP, here’s a short video from a developer and data modeler. He works with ABAP and data modeling:
Moving on, let’s look at which skills set strong SAP developers apart.
The Skill Set of SAP Developers and Assessing Potential Candidates
When you evaluate SAP talent, you shouldn't just look at resumes that list every module or tool. Only a sharp skill set aligned with your business projects will reduce hiring risk. So, these are the core areas to assess when you review a candidate profile or run technical interviews.
Technical Skills
Strong developers work across ABAP, SAP HANA, CDS views, Fiori/UI5, and OData services. They also understand middleware such as PI/PO or CPI, REST/SOAP APIs, and SAP API management. So, you should expect fluency in performance tuning, especially for S/4HANA and SQL-based environments.
Business Knowledge
Developers must understand how information technology supports processes across FI/CO, MM, SD, and HR modules. Without this foundation, code changes can disrupt financial closes, procurement flows, or supply chain tasks.
Debugging Under Pressure
You need candidates who can trace and fix issues during go-live or month-end cycles. Delays here can lead to missed revenue or compliance risks.
Soft Skills
78% of hiring managers report hiring technically strong candidates who later underperformed due to weak soft skills or poor cultural fit. To avoid this, look for clear communication with finance or HR teams and collaboration with consultants. Strong candidates also show adaptability when scope shifts and a problem-solving mindset that avoids quick hacks.
Continuous Learning
SAP evolves fast. The top developers track OSS notes, release updates, and migration guides to stay current. This habit reduces the risk of outdated solutions slowing down future upgrades or data migration projects.
Cultural Fit
Commitment matters, and 81% of hiring managers say culturally aligned candidates are less likely to leave. Developers who align with your culture and stay long-term save you from repeated rehiring. This stability protects your project timelines and reduces the hidden costs of constant onboarding and knowledge transfer.
Since that's out of the way, let’s walk you through how you should structure the hiring process to secure the right candidates.
9 Crucial Steps to Hiring a SAP Developer
Hiring SAP talent takes more than posting an opening and hoping the right profile shows up. You need a structured process that reduces risk, weeds out unqualified candidates, and proves each hire can perform under pressure.
These are the critical steps you should follow.
1. Define Project Requirements & Role
The first step is clarifying exactly what you need. You should identify which SAP modules are relevant. This includes FI/CO for finance, MM for procurement, SD for sales, or S/4HANA for ongoing transformations.
Next, decide if the role should be full-time, contract, or freelance. Document your scope, deadlines, and compliance needs. Then prepare a detailed job description covering responsibilities, required skills, and certifications.
Projects collapse when this foundation is weak. In fact, 37% of IT projects fail because objectives and milestones are not clearly defined.
2. Choose the Right Hiring Channel
Once the role is clear, select where to search for candidates. General job boards bring volume but not always quality. Specialized SAP recruiting firms, SAP partner networks, or tech boards like Dice and LinkedIn usually yield stronger results.
You can also use employee referral programs since internal networks typically surface trusted candidates. This channel can be powerful if used correctly. According to Boterview, while referrals make up only 6% of applications, studies show they account for almost 37% of hires.
Bar chart showing the impact of employee referrals on overall hiring success rates.
Source: Boterview
3. Source and Attract Candidates
Competition for SAP talent is intense, so your job postings must stand out. Show growth opportunities, modernization projects, and exposure to advanced systems like CPI or CDS views or Fiori.
Also, showcase your culture and work style because 76% of candidates want to understand company values before they accept an offer. So, make sure postings include SAP-specific keywords such as ABAP, Fiori, or S/4HANA to attract the right profiles searching for developer jobs.
4. Resume Screening & Shortlisting
With applications flowing in, you need discipline in screening. You can use an ATS (application review tools like Greenhouse or Lever) to filter resumes by key SAP skills. Look for “must-have” keywords such as ECC, ALE/IDocs, APIs, or integration tools.
According to ZipRecruiter, SAP ABAP Developer postings frequently list ECC, EDI, databases, web services, JavaScript, and SQL as required skills. Once you build a shortlist, confirm certifications and validate industry-specific project experience to ensure technical depth and domain alignment.
Bar chart comparing common keywords in SAP ABAP developer resumes and job descriptions.
Source: ZipRecruiter
5. Skills Assessment & Technical Tests
Resumes don’t demonstrate how candidates perform under pressure. That’s why you should run coding challenges in ABAP, Fiori/UI5, or integration scenarios. You can also use performance tuning exercises or case studies, such as building a custom report or debugging a failed IDoc, to evaluate problem-solving ability.
And you won't be alone doing this. Nearly 90% of companies now use at least one coding test in their hiring process. This proves the value of structured assessment. So, try to focus on tasks that measure practical thinking and efficiency under real constraints.
6. Interviews
Split your interviews into three layers, such as technical, soft skills, and cultural alignment.
Technical rounds should cover system integration, ABAP objects, debugging, and migration to S/4HANA.
Soft skills rounds should test collaboration and communication with finance, HR stakeholders , and functional teams.
Cultural rounds verify whether the candidate can adapt to your organization's values and work style.
Many employers admit this is where they struggle. According to TestGorilla’s recruitment data, 51% struggle to assess technical ability, while 53% face difficulty evaluating soft skills.
Infographic showing key challenges employers face in modern recruitment and hiring.
Source: TestGorilla
7. Background & Reference Checks
Once you identify a finalist, validate their professional track record. Call previous clients or employers to confirm delivery quality, problem-solving, and accountability. Structured reference checks often expose gaps a resume hides.
For sensitive roles, run a background check to cover compliance, data security, or regulatory risk. Many organizations already do this as well. Around 95% of companies do some form of pre-employment screening, which shows how critical this step has become.
8. Make an Offer
Prepare a formal offer letter that clearly outlines salary, benefits, and role expectations. Be ready to negotiate, especially for scarce skills like integration or Fiori development.
Research shows 73% of employers expect to negotiate initial salaries, so build that flexibility into your job offer extensions. Clear communication here prevents costly offer rejections or drawn-out delays.
9. Onboarding & KPIs
Securing the right developer is only half the job. You need a structured onboarding process with proper documentation standards, knowledge transfer, and assigned mentors.
So, try to define KPIs upfront. This includes code quality, bug resolution time, and delivery against milestones.
Without this structure, productivity lags. 44% of organizations report it takes over two months before a new developer is fully effective. So, linking onboarding to clear KPIs ensures your projects don’t lose momentum.
Pro tip: Planning your next SAP migration, but unsure where to start or what pitfalls to avoid? Read our page on SAP S/4HANA consulting to see how expert guidance can streamline your transition and reduce project risk.
Tips for Hiring SAP Developers
Hiring SAP talent requires both sound judgment and a structured process. The truth is, many technically qualified candidates still fail under project pressure because the vetting didn’t go deep enough. So, try out these practical checks to help you separate genuine experts from surface-level resumes.
Validate Module-Depth vs. Buzzwords
Many candidates claim broad exposure across modules like FI/CO, MM, SD, HCM, BW, and S/4HANA. But most use those names simply to pass automated filters. In fact, a study by interviewing.io found recruiters using resumes alone were accurate only 55% of the time in predicting interview-worthy talent (essentially no better than chance).
That means superficial signals like module listings won’t protect your project. Instead of asking, “Have you worked on FI/CO?”, ask, “Which FI/CO sub-process did you optimize last?" or "How did it impact reporting or month-end close?” This approach forces candidates to prove actual business impact.
Test Debugging Speed (Not Just Code)
Technical knowledge matters, but debugging skill is what saves a go-live from disaster. Around 20-40% of developer time is spent fixing issues. That means hiring someone who can debug fast is critical to avoiding days of downtime.
So, during interviews, give candidates a broken ABAP snippet or an integration error and time their process. Fast, structured debugging under pressure is worth far more than textbook-perfect syntax.
This is a skill that separates great developers from average ones; those who truly understand how code behaves in real environments stand out.
“The art of debugging is figuring out what you really told your program to do rather than what you thought you told it to do.” - Andrew Singer, Electrical Engineer and Associate Dean for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, University of Illinois
Screen for Cross-Generational SAP Knowledge
Most enterprise environments mix ECC, S/4HANA, and Fiori apps. Developers who’ve only worked on new systems can struggle when faced with legacy Z-programs still powering finance or logistics.
On the other hand, those who’ve only worked in ECC usually fall behind when confronted with CDS views or OData. The right hire must bridge both worlds. They need to understand how new frameworks interact with decades-old codebases that your organization still depends on.
Run a Business-Logic Test (Not Just a Technical One)
SAP sits at the intersection of technology and process. Developers who don’t grasp why finance or supply chain logic must be structured in a certain way will always create rework. To avoid this, you can give candidates a mock scenario, such as a sales order–to–invoice flow, and ask them to design the logic.
In a recent survey, 100% of people leaders listed business acumen and strategic thinking among their top three success factors. And nearly 90% named it their highest priority. Testing business logic upfront prevents costly misalignment between IT and finance.
Check Documentation Discipline
Bad documentation is one of the most expensive silent risks in SAP environments because it slows down every future change. Teams waste time decoding past work instead of delivering new features or fixes.
Research shows that clear documentation can lower software maintenance costs by up to 50%. That’s why evaluating a candidate’s documentation discipline is non-negotiable.
But you can make this right. During interviews, ask for a sample functional spec or technical design document (redacted for confidentiality) to assess how they structure technical work. If they can’t provide one, assume future maintenance costs will rise.
Stress-Test Their Integration Mindset
Modern SAP systems must connect seamlessly with platforms like Salesforce, Workday, Oracle, and various warehouse management tools. That means integration errors can ripple across finance, HR, and logistics.
So, ask candidates how they maintain data consistency across platforms. Strong answers reference middleware like PI/PO, CPI, ALE/IDocs, or APIs along with proper error handling practices.
Developers without integration discipline typically cause delays that break reporting and business intelligence dashboards downstream.
Simulate the Pressure Cooker
SAP go-lives are high-stakes, time-sensitive events that test composure and judgment. Since they're so important, you can use situational interviews like: “It’s go-live weekend. Finance can’t post invoices. Walk me through your next 30 minutes.”
The best candidates remain calm, prioritize triage, and communicate clearly with functional teams. Those who panic or resort to guessing are likely to fail under production pressure.
Verify “Upgrade & Migration” Experience
Many developers confuse “implementation” with “migration.” But migrations involve data cleansing, interface refactoring, and deprecated code handling. These are tasks unique to projects like S/4HANA transitions.
If you want to learn if they have the knowledge, ask them for specifics: “How did you handle Z-code or performance issues during your last upgrade?” If they can’t answer clearly, they may lack real migration depth.
Probe Their Vendor & Patch Awareness
SAP updates constantly through OSS notes, support packs, and hotfixes. Developers who ignore these patches can expose your systems to both downtime and risk.
One study found that 60% of data breaches exploit known vulnerabilities that already had fixes available but weren’t applied. So, ask when they last applied a note or patch and how they stay updated on releases. This test quickly shows who’s maintaining professional hygiene.
Cultural/Communication Test with Non-Tech Stakeholders
A developer’s core competence isn’t limited to coding. They must be able to translate technical changes into plain language. Hence, try to make them explain a program design to a “finance manager” or HR lead. If they can’t simplify without jargon, they’ll frustrate business users and slow decision-making.
A McKinsey study found that effective communication improves team productivity by up to 25%. This proves how much clarity impacts delivery. For distributed or global teams, this communication discipline becomes even more valuable in hybrid setups.
Pro tip: Want to get more value from your SAP agreements without costly surprises later? Read our guide on SAP contract negotiation to learn practical ways to lower expenses and strengthen your vendor terms.
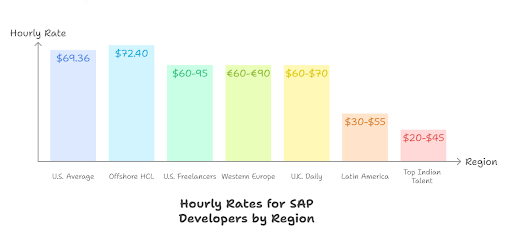
How Much Does It Cost to Hire a SAP Developer?
The cost to hire an SAP developer varies based on where you recruit, how experienced the candidate is, and whether you hire full-time or contract. Rates also shift between nearshore and offshore markets.
ZipRecruiter reports an average of $69.36 per hour for SAP developer roles in the U.S. Indeed lists offshore HCL developers at roughly $72.40 per hour. And Flexiple data shows broader ranges:
$60-$95 per hour for U.S.-based freelancers.
€60-€90 across Western Europe.
£500-£550 ($60-$70 per hour) per day in the U.K.
$30-$55 in Latin America.
$20-$45 for top Indian talent.
Bar chart comparing average hourly rates for SAP developers across different global regions.
Apart from base pay, you must budget for onboarding, training, software licenses, and recruitment fees. But here’s the thing: paying more for senior-level expertise often pays off in the long run. It reduces project overruns, code rework, and downtime during critical SAP upgrades.
KPIs to Measure SAP Developer Performance
Once you’ve built your SAP team, you need measurable indicators to see whether they’re delivering true value. The right KPIs help you separate high performers from those who slow progress or add hidden costs. The most effective ones are:
Code quality: Clean, reusable, and properly documented code that minimizes maintenance issues.
Bug resolution time: How quickly and accurately defects are fixed without creating repeat problems.
Delivery against milestones: Consistency in meeting agreed timelines and release schedules.
System performance: Measurable gains in transaction speed and error reduction after updates.
Knowledge sharing: How well developers document, mentor others, and transfer technical insight.
User feedback: Satisfaction levels from finance, HR, or logistics teams after go-lives or fixes.
Pro tip: Struggling to control SAP licensing costs or renewals without overpaying? Check out our SAP contract negotiation consulting services to learn how to secure better terms and avoid hidden expenses.
Solve Your SAP Hiring Challenges with Alpha Apex Group
Alpha Apex Group can help you fill important SAP roles faster and with greater precision. Our team combines SAP domain expertise with years of executive search experience. We find developers, architects, and leaders who fit both your project scope and company culture.
We’ve supported over 2,000 successful placements worldwide and maintain an average time-to-fill of just 43 days. That's 60% faster than the national average. Also, candidate profiles will reach your inbox within 72 hours. This allows you to act quickly without sacrificing quality.
Our proven process includes technical screening and culture alignment. We also provide advisory on future workforce planning for SAP S/4HANA transformations and hybrid environments.
From ABAP and Fiori developers to full ERP program leads, we connect you with professionals. They can help you strengthen your systems and reduce hiring risk. Partner with us to turn SAP hiring from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.
Take the Next Step in Building Your SAP Team
Hiring the right SAP developers is one of the most critical choices you’ll make for project stability and long-term ROI. Skilled talent reduces downtime, prevents migration delays, and protects your investment in core systems.
Partner with Alpha Apex Group to secure top-tier SAP professionals who deliver measurable results. Contact us today to strengthen your team, accelerate delivery, and maximize the value of your SAP investment.
FAQ’s
What is the difference between an SAP developer and an SAP ABAP developer?
An SAP developer works across multiple SAP technologies like Fiori, UI5, and HANA. An SAP ABAP developer focuses mainly on backend programming using ABAP within SAP systems.
How long does it take to hire an SAP developer?
Most companies need four to eight weeks to hire an SAP developer. The timeline depends on project scope, skill requirements, and how competitive the market is.
Do I need in-house or remote SAP developers?
In-house developers fit long-term ERP needs, while remote experts suit upgrades or short-term support. Many firms use hybrid teams for flexibility and cost efficiency.
Which industries rely most on SAP developers?
Industries like manufacturing, logistics, retail, finance, and healthcare depend heavily on SAP systems for planning, compliance, and data management.
What certifications should SAP developers have?
Look for certifications such as SAP Certified Development Associate – ABAP, S/4HANA, or Fiori/UI5 to confirm technical credibility and project readiness.
What’s the future demand for SAP developers?
Demand for SAP developers will stay high through 2030 and beyond, driven by global S/4HANA migrations and cloud adoption. As companies modernize legacy ECC systems, roles involving integration, analytics, and automation will expand.